I have been playing with Haskell and lately the Clash hardware compiler. Clash transpiles the functional hardware description written in Haskell to the standard HDLs such as Verilog. To be able to run such verilog code in an FPGA, a bitstream needs to be generated to program the FPGA. This post talks about a dockerized pipeline called Verilog2Fpga to do that.
Synthesis pipeline
Verilog2Fpga uses the existing open-source synthesis tools. It currently programs the iCE40HX1K-BLINK-EVN FPGA as that’s the one I happen to have.
- yosys - to synthesize circult netlist from the HDL
- nextpnr - for placing and routing of circuit components for the FPGA
- icestorm - to create a bitstream file with icepack for Lattice iCE40 FPGA
- icedude - to program the iCE40 evaluation board with the produced bitstream
How to use?
Linux
- Connect the FPGA via usb
- Setup docker container with
./setup_container.sh - Run
./synthesize.shwith a path to your verilog files (.v, .pcf) as an argument.
Eg:./synthesize.sh example_verilog
macOS / Windows
On macOS and Windows, the docker runs within a separate VM, so unlike linux, it can’t natively access the usb device. There are many ways this could be handled. Such as:
- Configuring the VM where docker runs
- Using tools like socat to forward usb data via TCP socket
How I configured for macOS
I use Mac so I faced this issue myself. I chose to install a separate linux VM (debian) with virtualbox instead of configuring with the above mentioned methods, mainly for ease. This is how I configured VM
1. Identify the usb device
- I ran
ioreg -p IOUSBin macOS which gave me the list of connected usb devices - To identify the acutal name of the device, I disconnected the FPGA and ran the command again. The device which disappeared from the list is sure to be the the FPGA device
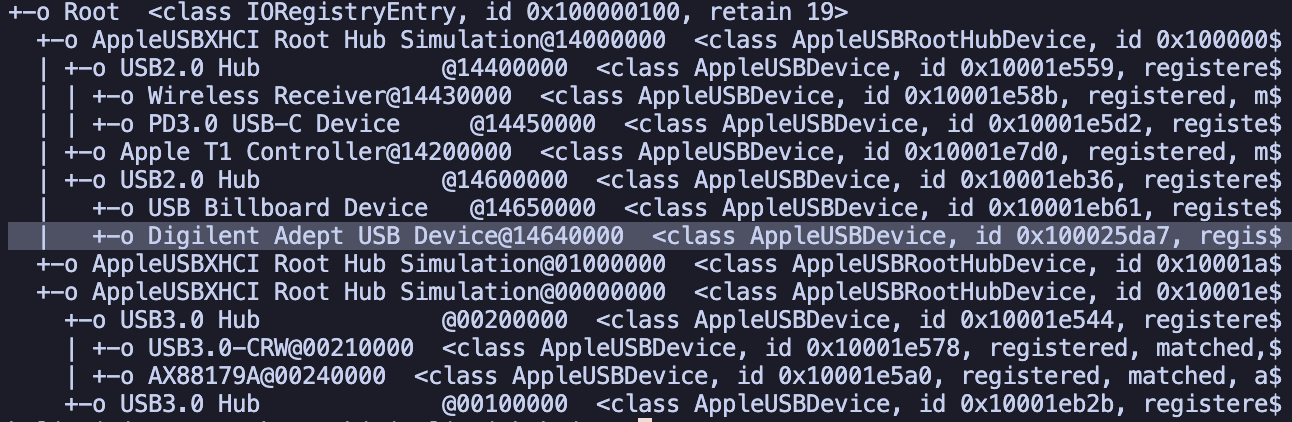
2. Configure the VM to access the identified USB device
With the device name known, I put it in the usb device filters of VM setting. Alternatively, I could have passed through all the usb devices but this gave me more confidence.
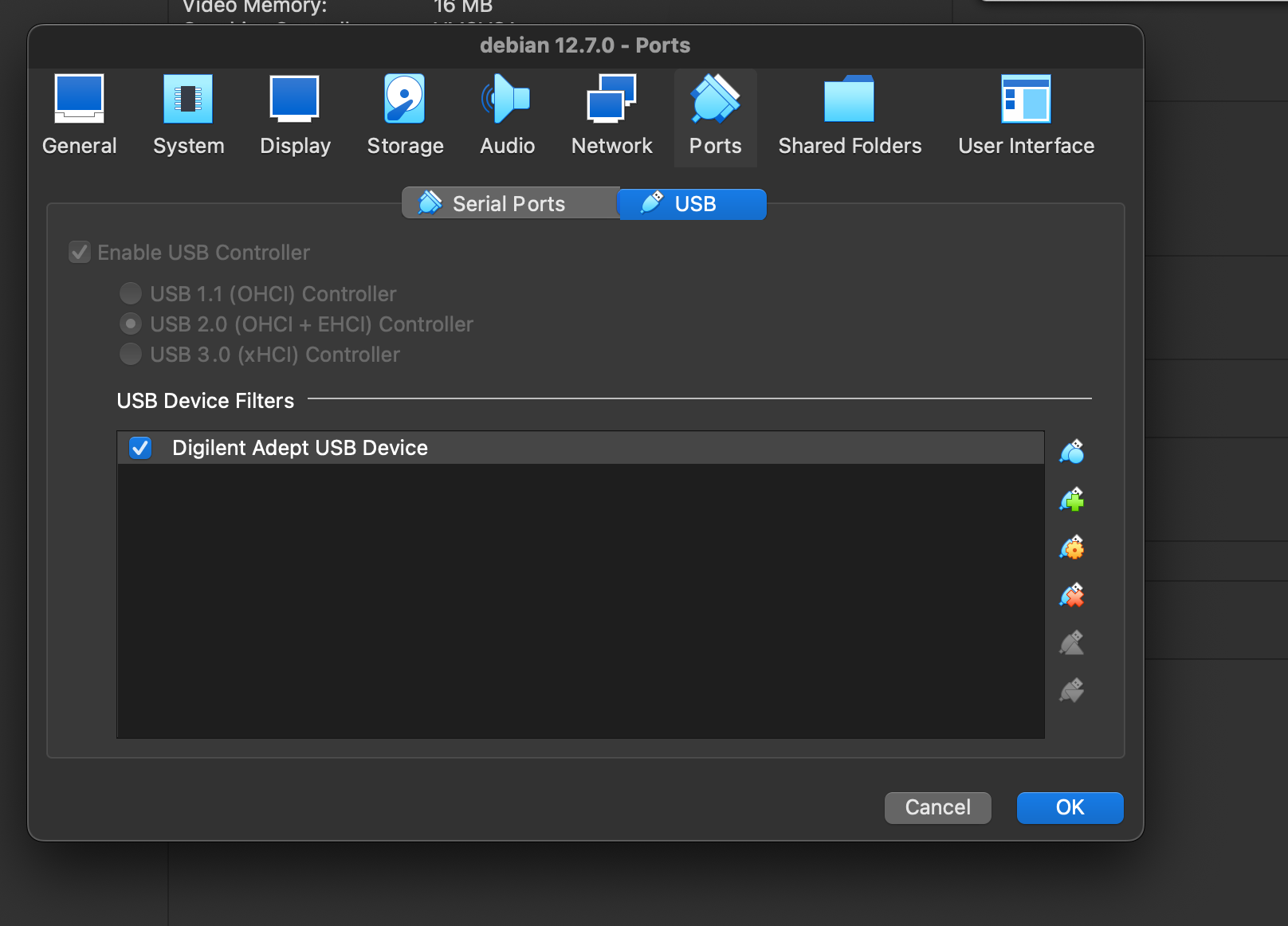
When the VM was running, I quickly ran lsusb to verify if it can access the usb device.
Running
After installing docker in the VM. I simply did:
./setup_container.sh./synthesize.sh example_verilog
and that was it.